
How Professional Teeth Whitening Treatments Work
Scientific Aspects of Professional Teeth Whitening Treatments
Professional teeth whitening treatments in the United States rely primarily on peroxide-based compounds to penetrate the tooth structure. Hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide are the most common agents used, breaking down into oxygen molecules that target both surface and deep-set stains. This reaction alters the color of staining substances through oxidation, resulting in a noticeable lift in tooth shade after even a single session.
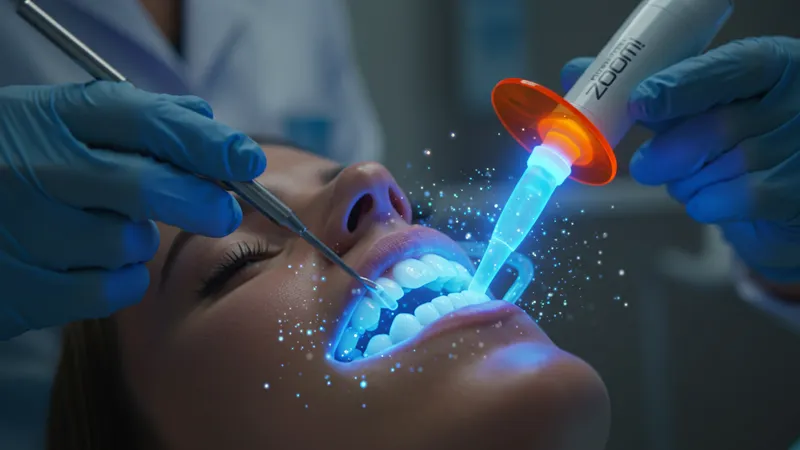
Zoom! Whitening, for example, amplifies this process using a proprietary light. The light serves to excite the peroxide molecules, accelerating stain breakdown and allowing for marked improvement in about 60–90 minutes. Patients who prefer a gentler approach might opt for Opalescence Boost, where the chemically activated gel works without any external light but is equally effective, especially for individuals with heightened tooth sensitivity.
The process is always controlled by a dental practitioner, who thoroughly examines the patient’s oral health before proceeding. This control minimizes side effects such as gum irritation or sensitivity, which may occur if stronger bleaches are misapplied. The practitioner also tailors the whitening agent’s concentration and application time for each individual, further improving the safety and predictability of the results.
In some cases, like with KöR Whitening, dentists combine in-office treatment with a custom-fitted take-home tray. This hybrid method extends the whitening process over days or weeks. By applying lower strength gel at home and a concentrated session in the office, patients achieve a seamless, bright smile suited for especially tough or aged stains. The science behind each step ensures consistent performance and predictable shade enhancement in American dental offices.